Earache in Children
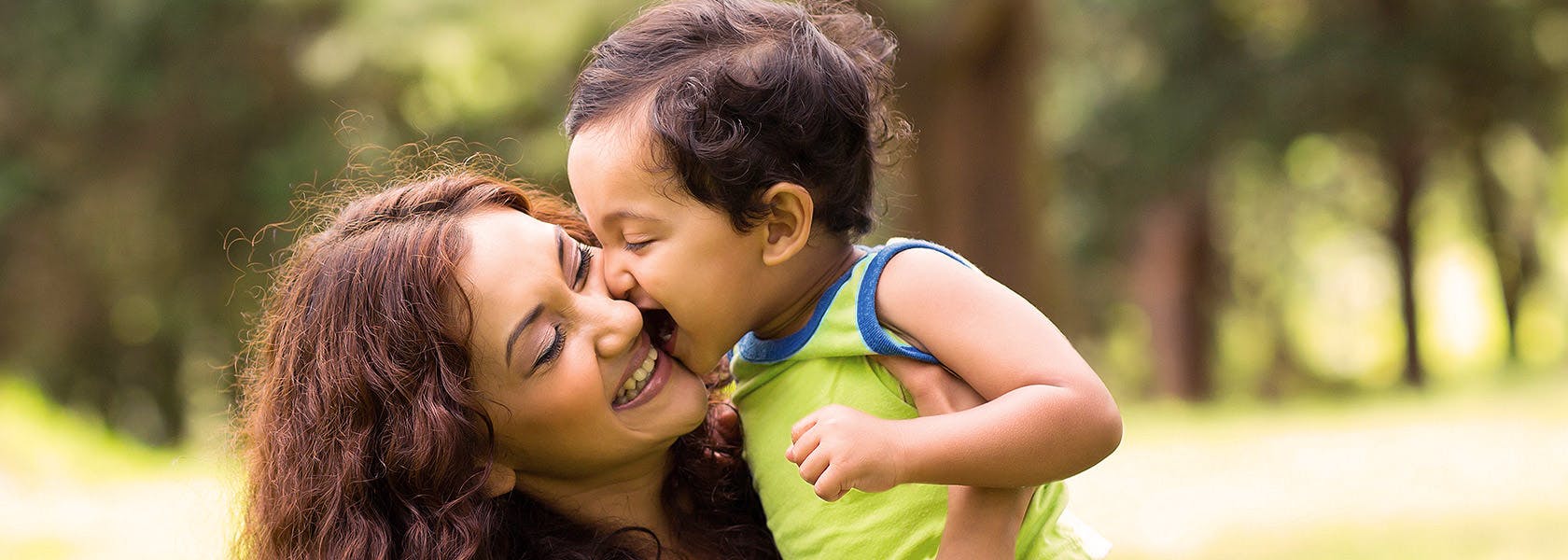
Earache is a common problem, particularly in children. A earache can be sharp and piercing, or dull and aching. There are many possible causes for an earache such as sinus infections, earwax, tonsillitis, and teeth grinding. But the most common ear infection is acute otitis media, or a middle ear infection, and is characterised by swollen and infected portions of the middle ear.
Managing And Treating Ear Infections In Children
Earache in children is common and one of the main reasons why parents take their children to see the doctor. In many cases the ‘ache’ can be due to an ear infection in the middle part of the ear known as otitis media.
What causes earache?
Otitis media is a result of an infection in the Eustachian tube. This thin tube connects the nose to the ear. When children get a cold, the Eustachian tube can become blocked, causing fluid to build up inside the ear which in turn results in earache.
Children are more prone to otitis media than adults because they are still building up their immune systems to fight off infections. Once a child reaches the age of around six years, ear infections are less common because the Eustachian tube is matured and less likely to become blocked.
Signs to look out for
The main symptoms of otitis media are:
- earache
- a high temperature
- headache
- ear discharge
- difficulty in hearing
- difficulty in sleeping
- loss of appetite.
In younger children who can’t explain what is wrong, otitis media is often difficult to detect. What’s more, it’s easy to dismiss the symptoms as general irritability or tiredness. Some signs include:
- pulling or tugging of the ear
- irritability
- restlessness at night
- poor feeding
- loss of balance
- fever
- tiredness or poor sleep
- difficulty in hearing.
Tips to manage ear pain in children
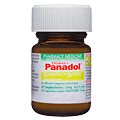
In most cases, otitis media clears up without any treatment within a few days. For home treatment, experts recommend using analgesics such as paracetamol for pain relief, as they can ease the pain of otitis media and help relieve fever. Aspirin should be avoided in children under 16 years who are suffering from a fever.